Platform Mapping Config Generation
Introduction
This document gives an overview of the vendor-provided configuration files needed to run FBOSS binaries on new platforms. Meta uses these files to generate a "Platform Mapping" JSON (used by wedge_agent and qsfp_service) and an ASIC configuration file (used by wedge_agent). The Platform Mapping JSON is built into FBOSS binaries and encompasses all lane mappings for connections between NPUs, external phys, and transceivers. It is used for programming the ports with the appropriate settings and includes all system ports with their possible speeds, lane configurations, and signal integrity settings.
This page first outlines the required structure of each necessary configuration file, then outlines the expected workflow for external FBOSS vendors to provide these configuration files and validate their settings through building / running FBOSS binaries.
Platform Configuration File Usage
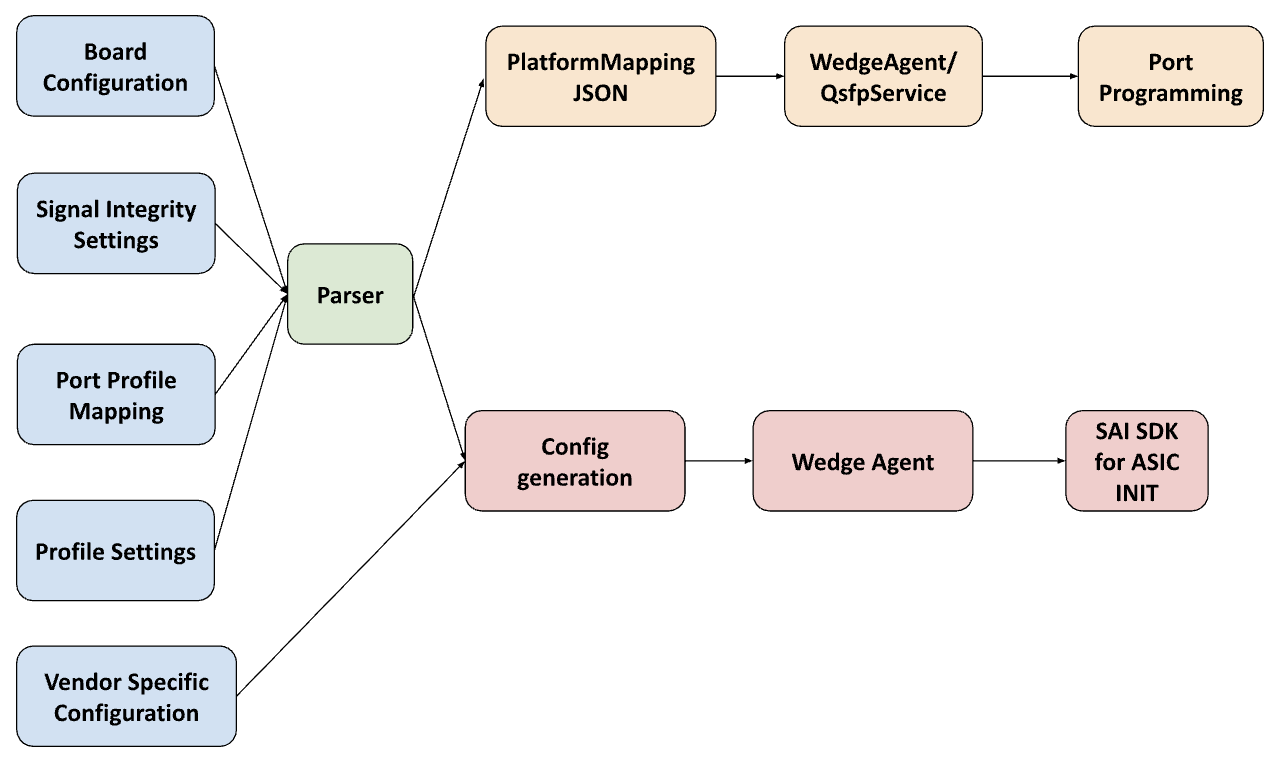
We expect vendors to provide the source files in blue, run the parser / config generation tool, and validate their Platform Mapping JSON before adding it to the FBOSS codebase through a pull request.
Source File Specification
Static Mapping (Board Configuration)
File: PLATFORM_static_mapping.csv (example)
This config file contains swap, polarities, and other board layout-related information.
- Enumerates all pairs of A->Z pins on the board.
- Represents the bidirectional pins connecting different hardware components on the board irrespective of the speed or any other configuration.
- Contains information about the TX and RX lanes, including the lane ID and PN Swaps.
Signal Integrity Settings
File: PLATFORM_si_settings.csv (example)
This config file contains the signal integrity settings like pre, post, and main for every port / serdes speed combination.
- Defines signal integrity configuration for all the hardware components on the board.
- Provides the ability to define settings for different factors. For example:
- Different settings for different lane speed.
- Different settings for copper vs. optic.
- Different settings for different copper cable lengths.
- Factors / settings not applicable for the board can be left empty.
Port Profile Mapping
File: PLATFORM_port_profile_mapping.csv (example)
This config file contains information about the ports that exist on the switch and what profiles each port supports.
Profile Settings
File: PLATFORM_profile_settings.csv (example)
This config file contains the information about what modulation, FEC, InterfaceType, etc., needs to be configured on different hardware components (NPU/XPHY) for different port speeds.
- Defines speed-specific settings. For example, for each speed, it defines the number of lanes used, FEC configuration that needs to be applied, Interface Type to be configured, etc.
- Each row is for an A->Z connection.
- For settings not applicable for any component, the cell should be left blank. For example, InterfaceType is not valid for the Transceiver component.
Vendor Specific Configuration
File: PLATFORM_vendor_config.json (example)
This config file contains vendor-specific configurations that are included in the wedge_agent configuration and passed directly to the SAI SDK during ASIC initialization. This file only contains information that cannot be derived from the other configuration files provided by the vendor. For example, this shouldn’t contain lane swap or polarity swap properties as that’s already derived from the static mapping file.
CSV Column Definitions
| Column Name | Definition | Valid Values |
|---|---|---|
| A/Z | Represents endpoints of two same / different hardware components. Any component / endpoint can be represented as A or Z side. | A, Z |
| A/Z_SLOT_ID | Unique ID of the FRU Slot that the corresponding chip is on. This is either 1 (for a fixed system) or the corresponding PIM / Linecard ID. | Range: >=1 |
| A/Z_CHIP_ID | Unique ID of the chip. For example, if there are two NPUs on the board, the chip IDs would be 1 and 2. Different chips can have the same ID. | Range: >=1 |
| A/Z_CHIP_TYPE | String defining the chip. | enum names |
| A/Z_CORE_ID | Unique ID of the core within the chip. | Range: >=0 |
| A/Z_CORE_TYPE | String defining the core. | enum names |
| A/Z_CORE_LANE | Unique logical ID of the lane within the core. For example, if a NPU Core has 8 lanes cores, the core lane ranges from [0, 7]. Lanes of different core can have the same lane ID but the lane ID within a core should be unique. | Range: >=0 |
| A/Z_PHYSICAL_TX/RX_LANE | Physical lane / serdes ID within the core. | Chip dependent |
| A/Z_TX/RX_POLARITY_SWAP | Polarity swap of the physical serdes lane. | Y, N |
| PORT_SPEED | Speed for the port (MBPS). | enum values |
| LOGICAL_PORTID | Unique portID associated to a port within a chip. | Range: >=0 |
| GLOBAL_PORTID | Unique portID associated to a port across the chips. For example - if there are two NPUs each with 100 ports, logical_portIDs range from 1-100 on both NPUs whereas global_portID ranges from 1-200. | Range: >=0 |
| MEDIA_TYPE | If the column is empty, the setting will be applied for both copper and optic media type. | COPPER, OPTIC, (empty) |
| CABLE_LENGTH | Length of the cable in meters the setting needs to be applied for – only applicable for copper media type. If the column is empty, the setting will be applied for all copper cable lengths. | Range: >=0, (empty) |
| A/Z_INTERFACE_TYPE | Interface type of connection. | enum names |
Platform Mapping Generation Workflow
Platform Mapping JSON Generation Tool
We provide a script to help external FBOSS vendors generate their respective platform_mapping.json file.
Prerequisites
Python 3 is required in order to run the helper script. You can install it via one of the below commands depending on which Linux distribution you're on.
Debian
sudo apt update
sudo apt -y upgrade
sudo apt install python3
CentOS
sudo dnf upgrade -y
sudo dnf install python3
Instructions
Platform mapping config generation is done via running the helper script below from the root of the FBOSS repository.
$ ./fboss/lib/platform_mapping_v2/run-helper.sh --platform-name XXX --output-dir XXX
Below are the command line arguments that are relevant to this script.
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| --platform-name (required) | Platform name that each CSV file has as prefix (e.g. montblanc in montblanc_static_mapping.csv). |
| --input-dir | Full directory path that has all vendor source files (default: fboss/lib/platform_mapping_v2/platforms/PLATFORM/). |
| --output-dir | Directory to write platform mapping config (default: fboss/lib/platform_mapping_v2/generated_platform_mappings/). |
| --multi-npu | Generates multi-NPU platform mapping config (default: False). |
To use this command, your input directory, either the default location or the one specified by --input-dir, needs to include the following files, with PLATFORM being a common string that identifies your platform:
PLATFORM_port_profile_mapping.csvPLATFORM_profile_settings.csvPLATFORM_si_settings.csvPLATFORM_static_mapping.csvPLATFORM_vendor_config.json
Validating Platform Mapping JSON
The first step in validing your platform mapping source files is to ensure a valid JSON is created in output-dir by running the above tool.
The second step is using this platform mapping JSON to ensure qsfp_service and wedge_agent binaries are brought up correctly. We typically have platfom mapping JSONs embedded into our FBOSS binaries, but to enable faster testing for external users, you can run both binaries with the --platform_mapping_override_path flag followed by the filepath to your platform mapping JSON – e.g. ./qsfp_service --platform_mapping_override_path /tmp/generated_platform_mappings/PLATFORM-platform-mapping.json.
Updating FBOSS Code to Use New Platform Mapping
Please refer to New Platform Support for instructions on how to incorporate this new Platform Mapping file within the FBOSS codebase.
If you are introducing a new platform, please also add your platform name to verify_generated_files.py.